
In terms of Latin and the declensions, it may mean we comment on what we see and express what we think of declensions to memorise them better and simplify learning, Linguistic: the ability to use language to understand others and express what we think.He suggests that there are several types of intelligence:
LATIN ENDINGS TEST ONLINY HOW TO
This theory is a tool used in educational science to allow every student to flourish, to learn to how to learn and help them think differently about their education.

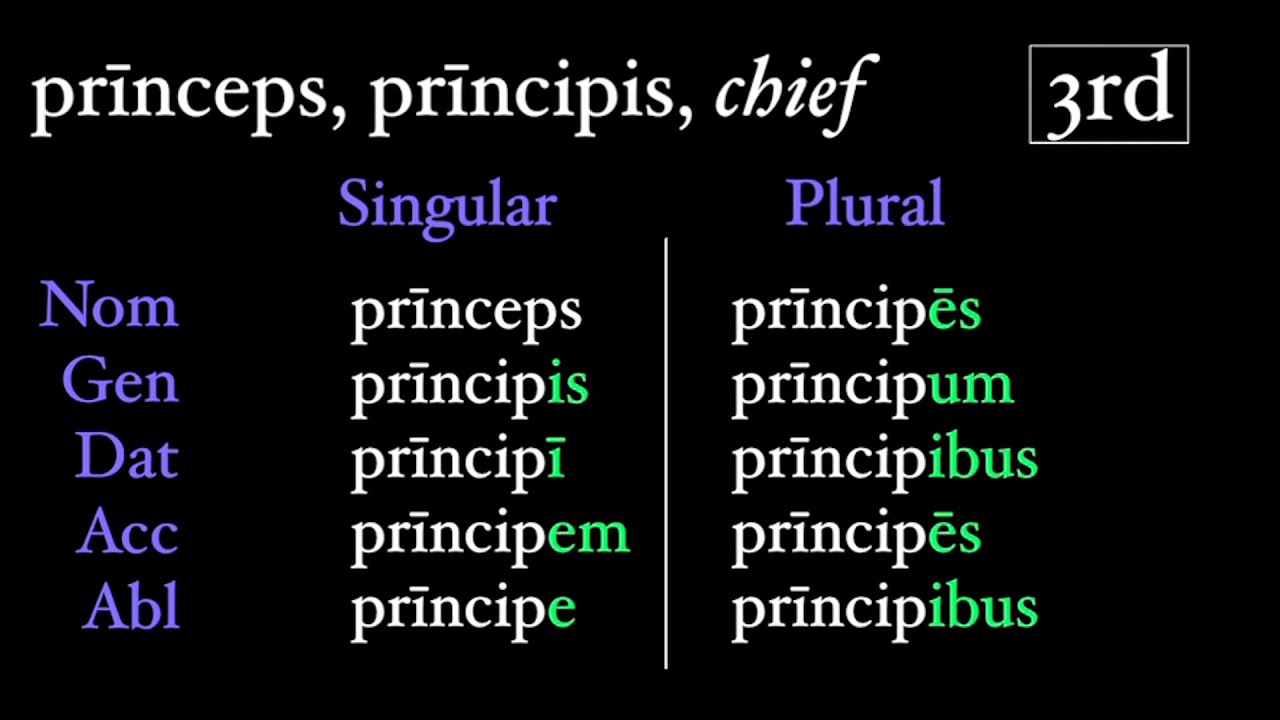
Source: Visual Hunt The theory of multiple intelligences was explained by the psychologist Howard Gardner in 1983 and later developed in 1993. Making a colour-coded diagram can help you remember the declensions. Latin Declensions: Learn Using Multiple Intelligences You can easily find all the Latin declensions in an English-Latin dictionary like the Oxford Latin Dictionary or even online. We will use the example of res, rei, f (thing): Case For the masculine or feminine parisyllabic nouns, the example used is civis, civis, m (citizen): Caseįor neutral parisyllabic nouns, the example is mare, maris, n (sea): Caseįor the imparisyllabic masculine or feminine nouns, the example we've used is consul, consulis, m (consul): Caseįor neutral imparisyllabic nouns, the example is corpus, corporis, n (body): Caseįor the fourth declension, masculine or feminine, we will use manus, us, f (hand) as an example: Caseįor the fourth declension for neutral nouns, we will use cornu, us, n (horn): CaseĪs for the fifth declension, there are only feminine nouns, with the exception of dies, ei, m (day) but which is also feminine when it means the date. For example: urbs, urbis (city) mens, mentis, f (mind) mons, montis, f (mountain) or cor, cordis, m (heart). Beware, there are false imparisyllabic nouns: these are nouns with two consonants at the end. What is it? Parisyllabic nouns have the same number of nominative and genitive syllables, whereas for imparisyllabic nouns, the genitive has one syllable more than the nominative. Indeed, there is a distinction between Parisyllabic and imparisyllabic Latin words. The third Latin declension is the most difficult to learn.

For the second declension for neutral nouns, the example is templum, i, n (neutral) which means temple: Case There are also nouns that are neutral in Latin. Here is the first declension: Caseįor the second declension in the masculine, we will use dominus, i, m (masculine) which means master or ager, i, m (field): Case


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
